What is the role of cryptography in the healthcare industry?
Here’s a bitter reality: Cyberattackers leave no individual or sector behind.
We know that data breaches and cyberattacks have become a reality today— thanks to technological evolution. However, the actual issue arises when critical services like healthcare become the target of malicious activities.
We’re not saying that other domains aren’t as important or that cybersecurity isn’t a concern for them. However, when it comes to healthcare, the stakes are not just high; they are exceptionally high. A breach in a hospital is not simply about financial gain or damage to reputation—it can literally be a matter of life and death. Patient records, real-time monitoring systems, and even medical devices themselves are at risk, putting countless lives on the fence.
So, how can we secure the medical or the healthcare system? Although there isn’t any one technique that provides guaranteed security, cryptography is critical to ensuring the integrity of our health system.
In this article, we will understand what cryptography is, its role in healthcare security, and how it helps protect sensitive medical data from cyber threats.
How vulnerable is the healthcare sector to cyberattacks?
The healthcare system is incredibly susceptible to cyberattacks, and the statistics show the real picture.
In 2024 alone, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recorded 677 significant health data breaches involving more than 182 million individuals. But what was the biggest reason behind these breaches? Hacking and IT incidents were responsible for 550 of the data breaches, leaking more than 166 million people’s information. The most severe of these was the Change Healthcare ransomware attack, which revealed the private data of 100 million Americans and messed with the entire nation’s healthcare services.
What is cryptography?
When you can’t afford to leak information, you need a way to protect it from cyber attackers— a way to encrypt messages that only trusted people can read. That’s what cryptography does. Cryptography is a way of securing information by converting it to an unreadable format that can only be read by those authorized by you.
It’s like sending a locked box with an important message inside, but unless you have the key to this box, you can’t read the message. That’s encryption, which secures items such as patient files, passwords, and online transactions from hackers.
Even if a hacker gets hold of the information, they won’t be able to decipher it unless they have a proper key.
That being said, cryptography isn’t exactly about hiding the information; it also ensures that the data is not changed or altered in transit.
Cryptography is an important technique in the security framework of any organization in any industry, particularly in the healthcare sector. It secures patients’ electronic health records (EHRs), protecting medical devices and safeguarding patient data from cyber threats. Keeping these records secure not only means one less thing to worry about, but it is also about maintaining the integrity of your hospital or medical facility.
How does cryptography keep communication safe in the healthcare industry?
Post the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine and remote patient monitoring are no longer a far-fetched reality; they have become an integral aspect of the industry. While this collaboration of digitization and healthcare has transformed the industry, it has also opened the doors to various vulnerabilities.
To safeguard your organization and your patients’ data from cyberattackers, cryptography ensures that all communication remains secure, confidential, and tamper-proof. Here’s how:
Hashing— Making sure the data is protected
Patient data is very important in the healthcare industry, which is why it must remain secure. To ensure this, cryptography uses a hashing algorithm, which is like a unique fingerprint for data. Hashing turns patient data into a fixed-length character string that can easily identify any tampering or alteration. If any alteration is made to the original data, even the smallest one, the hash value will be drastically different. This helps make patient records intact and reliable.
Encryption— Protecting data from unauthorized access
In medicine, we all know that you cannot afford to lose sensitive patient information such as medical records and test results. It must remain safe and away from the reach of attackers. Cryptography makes it happen through encryption.
It works by converting readable data into an unreadable format that only authorized people can decode using a decryption key. If someone who does not have the key tries to access the data, they won’t be able to understand or decode it.
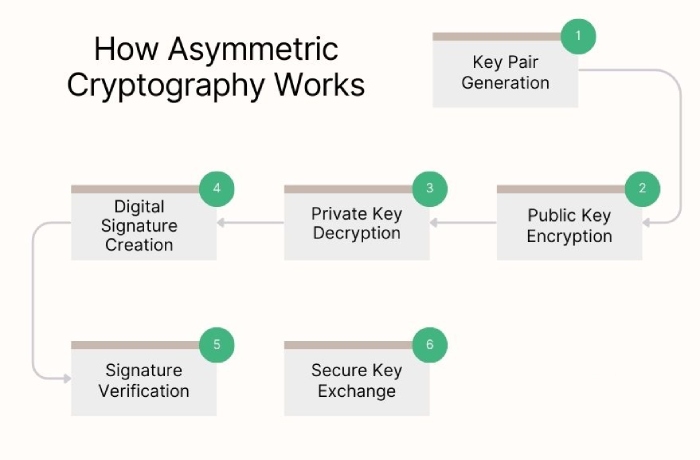
Digital signatures— Verifying authenticity
Digital signatures help in verifying that a document or message is authentic and has not been tampered with. To confirm this, they employ asymmetric cryptography. Here’s how they work:
So, in digital signatures, there are two keys— one for signing and the other for verification. When the document is signed by the sender using a private key, the recipient verifies it using the public key. They’re primarily used to protect prescriptions, insurance details, medical history, and communication between physicians, patients, and hospitals in healthcare.
SSL/TLS— Keeping online conversations safe
You may think that a telephonic conversation between a doctor and a patient might be of no good to an attacker aiming to pull off a cyberattack, but this isn’t true. They can misuse this conversation in so many ways.
To protect online conversations from being intercepted by the bad guys, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) encrypt their conversations. This stops hackers from spying on private medical discussions. So the next time you see “https://” before a website, know that your connection is secure.
Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC in healthcare email communications ensures that sensitive patient data remains secure by preventing email spoofing, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) – Controlling who gets access
In the field of medicine, one has to be extra careful about who gets access to what. You cannot trust anyone with critical, sensitive data. This is why you need cryptography. Cryptography works on public key infrastructure (PKI), which helps ensure that only the right people have access to sensitive medical data. This way, your medical institution can keep all the important data safe, including electronic health records, prescriptions, and other critical medical information.