Bybit’s $1.5B Loss, FatalRAT Hits APAC, GitVenom Targets Wallets, – Cybersecurity News [February 24, 2025]
State-sponsored hacktivism is on the rise. Script kiddies use pre-existing scripts while others employ highly sophisticated tactics using diverse tools and resources. Attackers are scouring GitHub for sensitive information on GitHub and trying to steal critical information from repositories. Security breaches happen when they gain unauthorized access to the source code. This week, we’re reviewing a series of the latest cybersecurity incidents by closely analyzing their attack trends and threat vectors. We’ll also discuss how a significant cryptocurrency exchange organization was the victim of a massive crypto attack and explore how the FatalRAT malware targeted organizations across APAC. Below is a summary of the latest findings.
Bybit Faces $1.5 Billion in Cryptocurrency Losses
Bybit organization suffered one of the most significant cryptocurrency cyber attacks in history. The breach targeted Bybit’s Ethereum Multisig cold wallet, causing USD 1.5 billion in losses in ETH (Ethereum) and stETH (Staked Ether). Malicious threat actors exploited a vulnerability in the transaction signing and manipulated smart contract logic. This compromised vulnerability allowed them to deceive approvals and evade fraudulent transaction detection systems, making it harder to detect in the early invasion stages. The attackers executed unauthorized cryptocurrency transfers to unidentified wallet addresses, convincingly to the attack owner’s address!.
Customers are reassured that the organization holds over $20 billion in Assets Under Management (AUM). If required, it will request for bridge loan assistance. Bybit is currently hardening multisig wallet security and conducting frequent audits for its smart contracts. The FBI has warned global organizations of non-phishing hijacks by issuing a public advisory on February 25th, detailing information about the latest ghost ransomware. All other existing cold wallets remain safe and fortunately have not been attacked. And the good news is that withdrawals are not entirely halted.
However, the high volume of fraudulent transactions may cause delays in customer service. Bybit is committed to maintaining the integrity of its platform. Its reserves are substantial and 1:1 backed. 70% of their pending requests have been processed and all their other services, including trading products, cards, and P2P, are fully operational.
FatalRAT Malware Exploits Cloud Services and Targets APAC
Recent news headlines suggest, FatalRAT Malware targeted industrial organizations across the APAC (Asia Pacific) region. According to the authentic sources, it launched phishing campaigns towards transportation, construction, IT, healthcare, energy, and telecom domains. Attackers allegedly bypassed detection measures and distributed malware using cloud nodes and CDN services. They successfully infiltrated and ran payloads. How did the attack materialize in the 3D? They primarily sent phishing emails with ZIP attachments.
Victims opened these files and a first-stage loader was executed automatically. Progressively, it retrieved DLL files and a FatalRAT configurator. DLL acted as a second-stage loader, and allegedly fetched the payload from the existing cloud service. Moving on to the next step, the configurator downloaded additional required data. Finally, the malware stealthily executed and displayed fake error prompts to users.
Cybersecurity adversaries steal browser data, install keyloggers, and deploy remote administration tools. They run virtual machines and sandboxes, and the malware auto-terminates when it detects multiple security checks. Businesses are advised to critically harden their email security operations and avoid installing suspicious files and attachments from unidentified sources. Other standard techniques used in this campaign included dynamic changes in the command and control (C2) addresses, native file hosting CDN, and publicly available packers for sample encryptions.
GitVenom Uses Fake GitHub Projects to Attack Currency Wallets
Hackers are getting creative by creating hundreds of GitHub repos and tricking targets by luring them with fake code. The scam looks too real and victims end up falling for it.
They create Telegram bots for Bitcoin wallets, Valorant cracking tools, and Instagram automation solutions. Infected and fake repos contain information about the projects, including how to compile them. Hijackers also add multiple tags and artificially inflate the number of commits made to them. They place timestamps which automatically update every few victims.
Python, JavaScript, C, C++, and C# are used to create them. They steal Personal Identifier Information (PII) and hijack cryptocurrency transactions. Kaspersky exposed hidden malware that stole personal data worth $485,000 on GitHub. Businesses are urged to verify the authenticity and security of open-source codebases before downloading and executing files on local systems. The subject-matter experts around the globe are warning that such alleged fake repositories often include malicious code, that is tailor-designed to execute unauthorized commands that hold the power to exfiltrate sensitive data from the targeted systems.
The hackers are continuously working round the clock to refine their attack tactics and vectors. The resultant of these man-hours is making it harder for automated detection systems to flag these malicious repositories. But as it’s rightly said, “Where there is a will, there is a way”, the organizations and industries can leverage the use of multi-factor authentication to help combat these security challenges.
International HackersGroupTarget Healthcare with Philips DICOM Viewers
Cybersecurity adversaries now target healthcare agencies using malicious code installers known as DICOM. Once executed, these installers deploy a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) to create a backdoor in the victim’s system. Hackers can stay in their networks indefinitely and the group can deploy malware via text message-based attacks, SEO poisoning, and social media. Researchers have identified 29 malware samples impersonating DICOM viewers, with activities tracing back to December 2024.
The infection process unfolds in three stages: Attackers download additional malicious files from a compromised cloud repository. In the second stage, “ValleyRAT” payload turns off antivirus protection. For the third, it installs a cryptocurrency miner and keylogger. Patient privacy is a serious concern. The campaign puts hospitals in grave danger and impacts “hospital-at-home” programs, where vulnerable devices connect directly to hospital networks. Healthcare agencies must refocus their security controls. They must deploy ongoing threat monitoring to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information.
However, the group does not engage in direct extortion but is financially-motivated. They have been suspected of mimicking other healthcare apps and distributing malicious software versions, but no solid evidence has been found yet. Their goals are distributing their malware as far as possible, reaching gaming applications, and disguising ValleyRAT for the Windows text editor EmEditor, systems drivers, utilities, and beyond.
EncryptHub Hits 618 Organizations, Spreading Infostealers & Ransomware
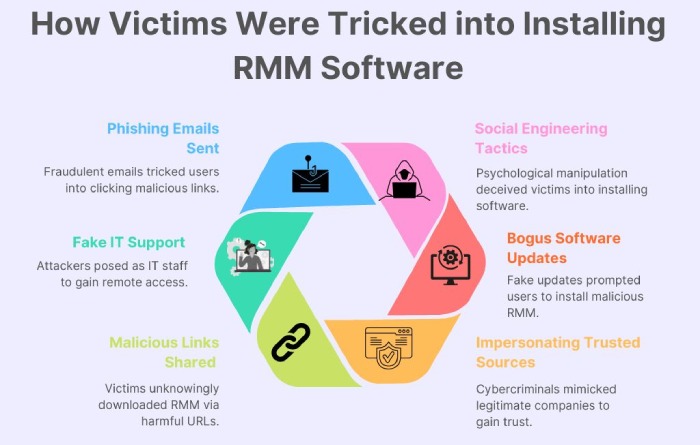
Recently, EncryptHub allegedly breached 618 organizations with phishing and ransomware social engineering attacks, turning tables upside-down. Since 26 June 2024, LARVA-208 (EncryptHub) has launched various spear-phishing attacks. It carried out different operational strategies to obtain initial access via vishing and smishing (SMS phishing). Victims were tricked into installing remote monitoring and management (RMM) software on their systems.
Step 1. Create a phishing site to obtain the victim’s VPN credentials.
Step 2. Call up the victim due to a technical reason.
Step 3: Pose as an IT team staff member or help desk.
Step 4: Victim falls for an SMS text message.
Step 5:Adversaries run various stealers on their compromised machines by using PowerShell scripts written by them.
How did they do this? Let’s understand how:
Actors use multiple tactics such as fake login pages, open URL redirection, social engineering, and others, to bypass MFA. This way, LARVA-208 deployed ransomware payloads and managed several domain acquisitions.. Organizations must educate employees about these schemes, incorporate strong authentication, and apply the best endpoint security solutions to stay protected. Regular security audits, network monitoring, and incident response planning can help spot and prevent these issues before they cause irreversible damage.