FrigidStealer Targets macOS, MAVInject Evades Detection, Stealthy Espionage Malware – Cybersecurity News [February 17, 2025]
Cybersecurity threats are rapidly evolving at an unprecedented rate, making cybersecurity more critical than ever. This week, we uncovered a new malware targeting macOS users through fake browser updates and a stealthy cyberattack exploiting Windows utilities to evade detection. We will also explore how hackers deploy payment skimmers using hidden image tags, as well as discover how the latest cyber espionage campaigns target big industries and international corporations. Lastly, we will cover the news highlighting recent data breaches affecting thousands of individuals and organizations across the globe.
New FrigidStealer Malware Targets macOS via Fake Browser Updates
Cybersecurity researchers have identified a new macOS malware, namely FrigidStealer, which spreads rapidly leveraging fake browser update pages. The malware comes with cross-platform compatibility, wherein it can attack across different platforms, including Windows and Android. According to the findings, it is fair enough to link this malware to a recent campaign being allegedly operated by TA2727 threat group actors. These security-related attacks first exploit web applications by tricking users into downloading malicious payloads, eventually providing backdoors to the user’s systems.
According to the news sources, the alleged threat actor group TA2726 played an essential role in spreading malware. It acted as a traffic distribution system (TDS) for multiple suspected cybercriminal groups, including TA2727 and TA569, which distributed SocGholish (FakeUpdates) malware. These malicious updates disguised themselves as legitimate browser updates in Chrome and Edge software platforms, to name a few, delivering different malware custom-tailored to attack users based on their active device and location.
As of January 2025, the campaign has historically infected many macOS systems to date, redirecting users to fake update page links to download FrigidStealer. This Go-based malware leverages AppleScript to request system passwords, gaining elevated privileges to steal browser data, Apple Notes and cryptocurrency-related sensitive credentials.
Hackers Exploit MAVInject.exe to Evade Detection in Recent Cyber Attacks
Cybersecurity researchers have identified a covert cyberattack technique leveraging a legitimate Windows utility, MAVInject.exe, to inject malware into targeted systems while successfully refraining from getting caught by existing detection mechanisms. The attack allegedly was carried out by a state-sponsored threat group initially aimed to sneak into antivirus programs to install dangerous payloads while maintaining its anonymity throughout the attack cycle. The attack is first initiated with a dropper program that downloads several files simultaneously, including a fake PDF document. Then, the malware sideloads a rogue DLL file through a legitimate gaming application, injecting a modified backdoor for remote access.
One important thing to note is that the key function of the malware is to check for running security processes. Lastly, MAVInject.exe is used to execute malicious code if a targeted antivirus is detected in the process. With the approaching final step, the malware is then connected with a remote command server, which enables attackers to exfiltrate data, execute commands, and maintain stability.
Experts note that the injection technique is not entirely new but remains effective against outdated security defenses. The group behind the Revivalstone campaign is reportedly revisiting and iterating on its methods of attack to strengthen the robustness of its attack mechanisms In the hour, cybersecurity professionals are emphasizing the need to enhance endpoint security so that the security controls become strong enough to fight against advanced threats.
Stealthy Cyber Espionage Campaign Targets Firms with Advanced Malware
Cybersecurity researchers have recently uncovered a cyber espionage campaign allegedly targeting manufacturing, materials, and energy firms using a recently tested stealth malware toolkit. As reports from authentic sources suggest, this campaign, called RevivalStone, allegedly exploited SQL injection vulnerabilities in enterprise systems, allowing attackers to gain persistent remote access and exfiltrate critical data.
These malicious threat actors used a multi-layered approach. First, they compromised servers with web shells like China Chopper and Behinder, then expanded their reach by breaching managed service providers (MSPs) to infiltrate multiple organizations at once. The campaign’s latest malware strain leveraged advanced evasion techniques, encryption updates, and legitimate digital certificates to bypass security defenses.
Notable malware variants deployed in this attack included DEATHLOTUS, CUNNINGPIGEON, and WINNKIT, each designed for backdoor access, network interception, and system manipulation. References to StoneV5 and TreadStone implied that this malware family is still in its nascent stages and is actively evolving. Robust malware protection, including threat detection, endpoint security, and monitoring, is key to mitigating evolving threats.
Hackers Exploit Image Tags to Deploy Stealthy Payment Skimmers
Recently, cybercriminals secretly injected payment skimmers into e-commerce websites by using malicious image tags to steal sensitive credit card details. This sophisticated attack disguised malicious JavaScript code inside ‘<img>’ tags and they very intelligently used the error event to trigger execution, which usually pops up when an image fails to load. This malware first targets checkout pages and waits for users to submit their full payment details before sending stolen card numbers, expiration dates, and CVVs to another external server. Hackers very tactfully hide harmful code inside an image tag, which allows them to trick security scanners and make it much harder to detect.
This above-suggested method avoids the use of traditional malicious tactics that were used similarly for the purpose, earlier, the infected code was directly injected into form fields, which created a disturbance in the code execution and therefore had higher risks of increasing the likelihood of user alert. The attack picture we just painted, to our astonishment, is just one side of the coin such similar techniques are employed against WordPress websites, where alleged threat actors and groups simply implant backdoors inside important plugins, researchers said.
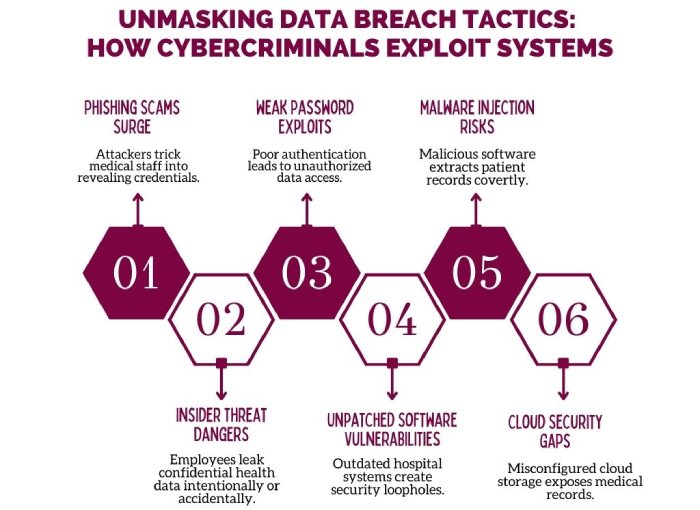
Major Data Breaches Expose Sensitive Information in Recent Cyberattacks
Data breach attacks, nowadays, are gaining increased popularity and creating hype in the cybercriminal world. According to the authentic news sources of HIPAA researchers, two massive data breaches have been recently confirmed and acknowledged. The security attack exposed sensitive information, including multiple users’ PII (Personal Identifiable Information) and medical information. So, what was the threat vector they employed for the malicious deed? Malicious actors allegedly hacked into critical systems by heavily leveraging the use of modern invasive tactics, techniques, and methodologies.
As the news suggests, they passed with flying colors and impacted millions in figures. According to the reports, the data unlawfully accessed contained names, social security numbers, driver’s licenses, and financial details. The targeted authorities have confirmed to provide those affected individuals with free credit monitoring and identity theft protection while extra security measures have been implemented to stop future occurrences.
In another recent incident, a medical service provider detected unauthorized access to its systems between February 21 and March 1, 2024, resulting in the potential exfiltration of patient records. Exposed information included medical records, financial data, and personal identification details. While no misuse had been discovered, credit monitoring services had been extended as a precaution. As the news sources suggest, officials continue to assess the full breaches of affected individuals to monitor their financial and medical records.